查看完整案例

收藏
下载

翻译
"'Everything is a number' Pythagoras. The Problem: Given a limited number of bricks to build a house between party walls, find the most appropriate shape in order to construct the largest area with the smallest perimeter.
Solution: Deductive logical method. Premise 1 - Any transformation of the shape generates an increase in surface area. Premise 2 - The appropriate shapes between party walls are right-angle figures. Conclusion - The optimal shape is a pure prism with a rectangular base.
Mathematical method: Area = X.Y Y = A/X // Perimeter = 2X + 2Y P = 2X + 2A/X // F(x) = 2X + 2A/X We differentiate the perimeter function with respect to X and set it equal to 0 F'(x) = 2 - 2A/X^2 F'(x) = 0 0 = 2 - 2A/X^2 0 = 1 - A/X^2 X^2 = A X = √A // If X = √A and Y = A/X then Y = A/√A Y = √A Y = X
Second derivative to determine the maximum or minimum. F''(x) = 4A/X^3 F''(x) = 4A/√A^3 F''(x) = 4√A/A > 0, therefore the perimeter is minimum. Conclusion: The maximum area with the smallest perimeter is a rectangle with equal sides, that is, a square.
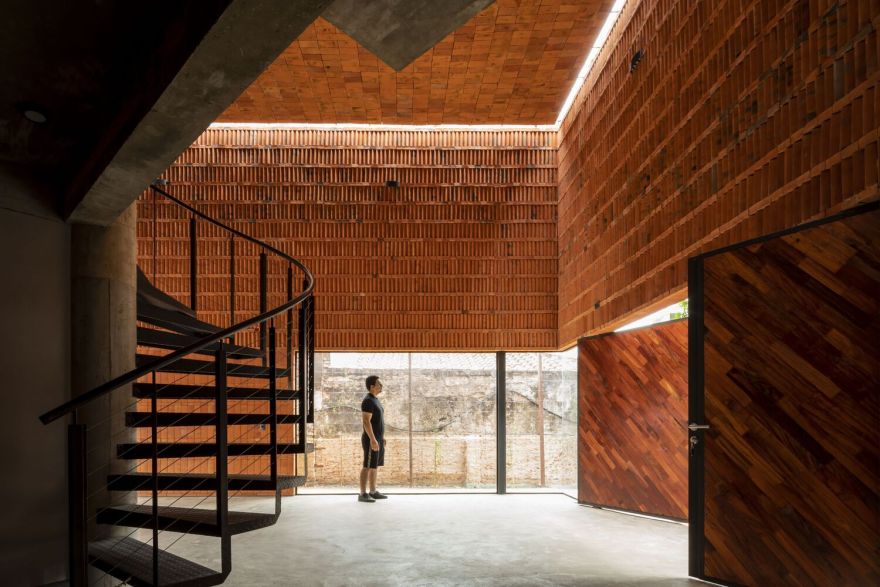
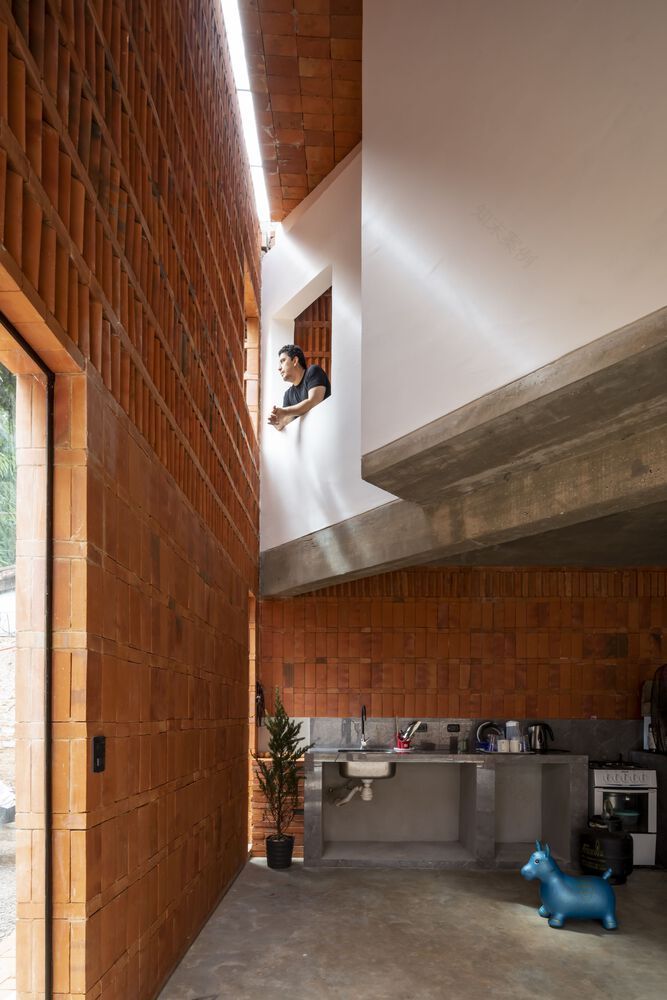
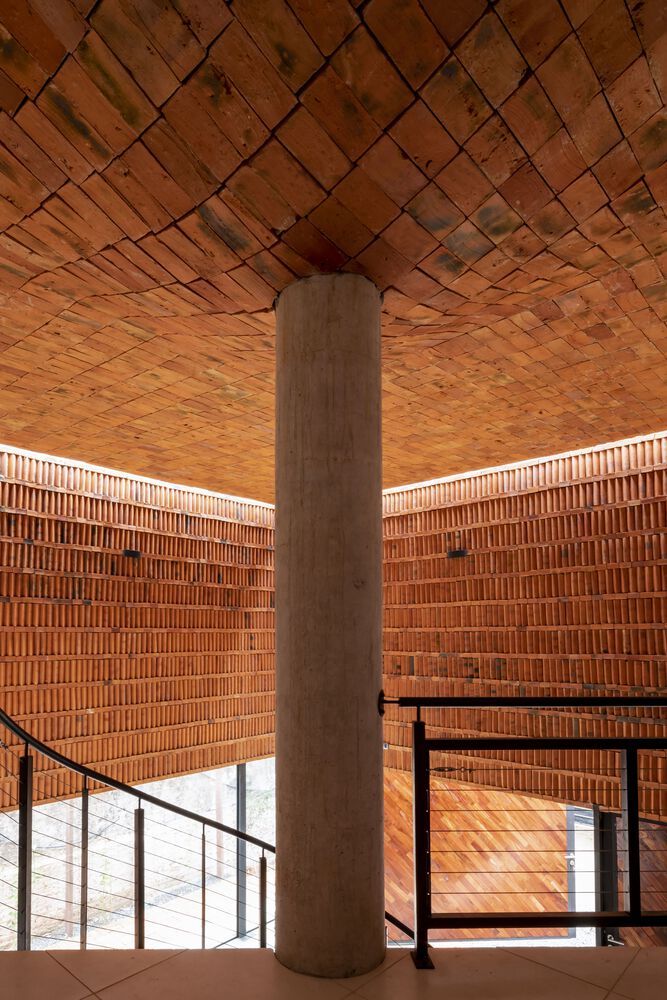
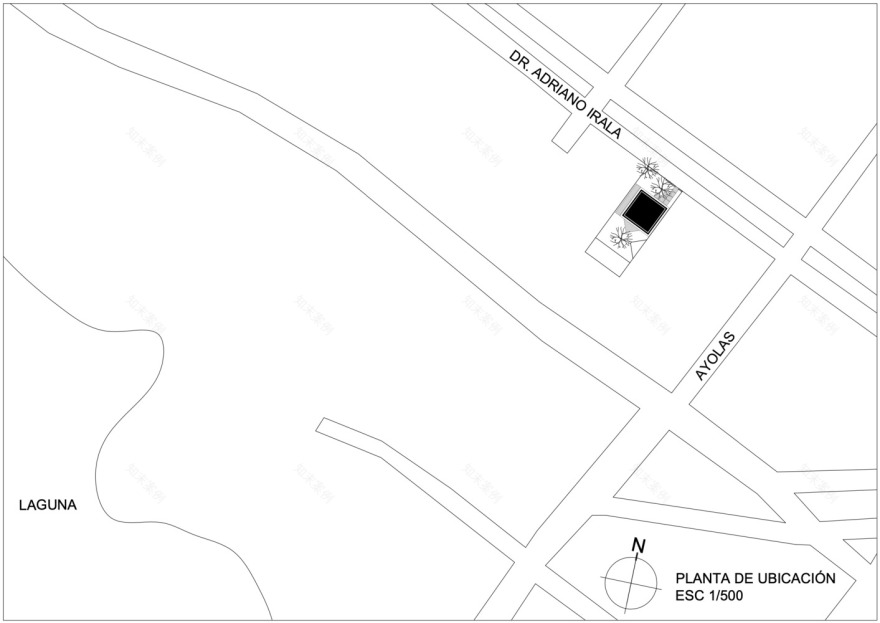
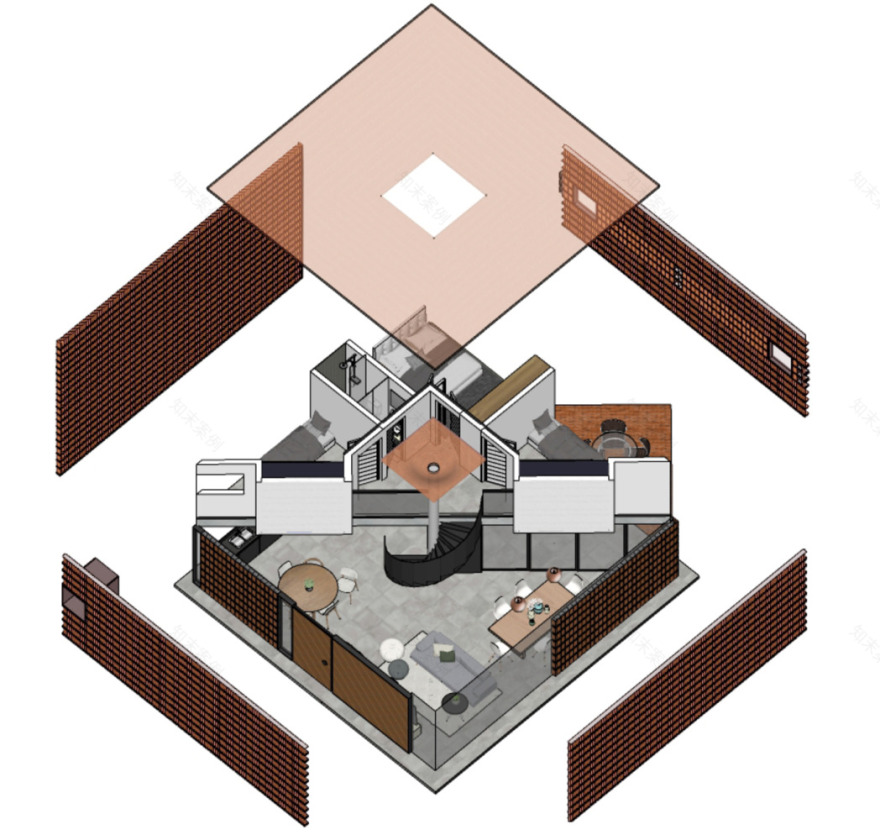
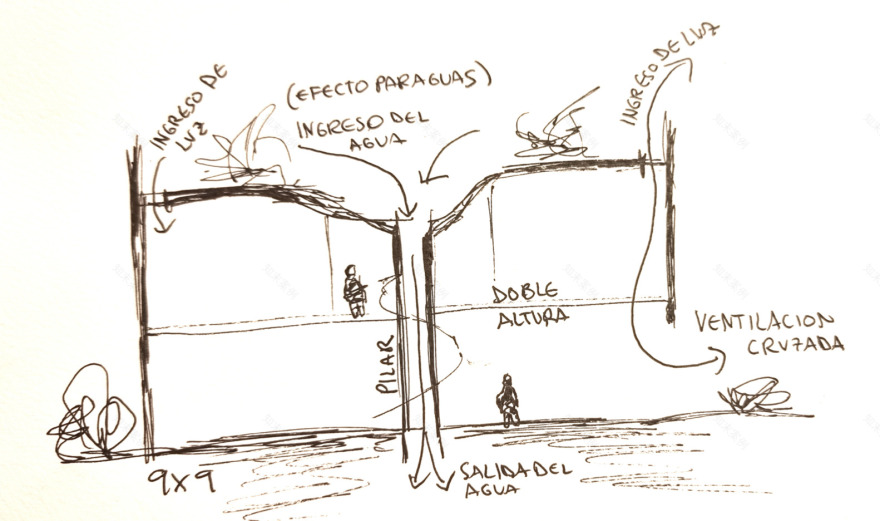
A pure prism with a square base is projected onto a foundation slab that functions as both structure and floor. A minimum necessary area is established for proper functionality and a maximum area is based on the stated problem. Geometric figures are inscribed in the floor plan within the prism, pivoting on a central pillar that articulates the elements and orders the space.
The space is constructed with walls and ceilings made of visible ceramic bricks with dry joints using polymeric adhesive, avoiding waste and undesired joints. The atmosphere is created through careful and excellent management of light. If the number excites, is it Architecture or Construction?"
客服
消息
收藏
下载
最近