查看完整案例


收藏
下载
宜兴城市污水资源概念厂,是将传统污水处理厂升级打造为资源循环工厂的重要实践项目,也是减少污水处理厂的邻避效应,将传统封闭的治污工厂变为环境友好、对公众开放、融于环境、科普教育,面向未来的可持续基础设施,也是将传统治污工厂升级为生态友好型、资源再利用型的现代概念工厂。
▼视频,video ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
The Concept WRRF Yixing, is a future-oriented Water Resource Recovery Facility & factory. The aim of the project is to upgrade conventional sewage treatment plants to environmental-friendly and recycling-oriented plants. Alleviating the Not-in-my-backyard effect, the upgrade will transform a closed pollution-control plant into a sustainable and future-oriented infrastructure project that is environmental-friendly, open to the public, harmonious with its neighborhood and available for science education.
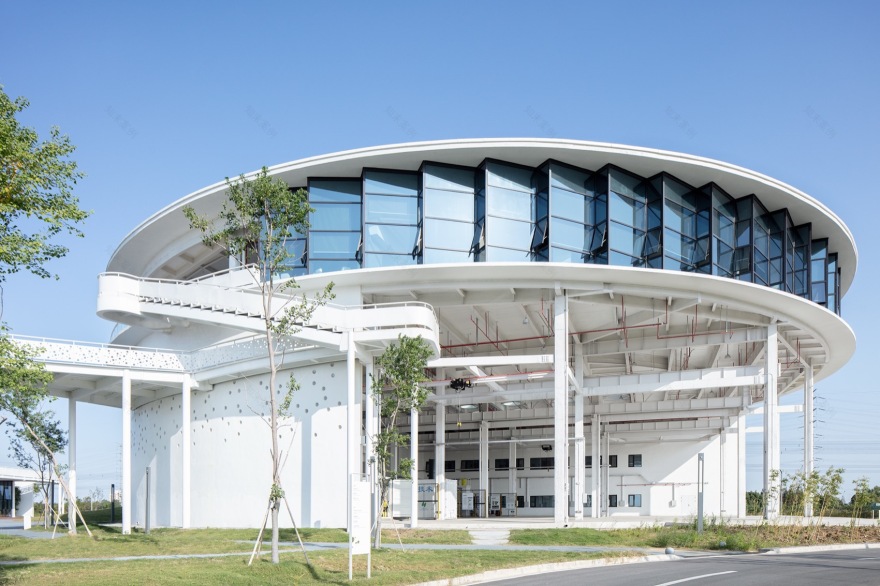
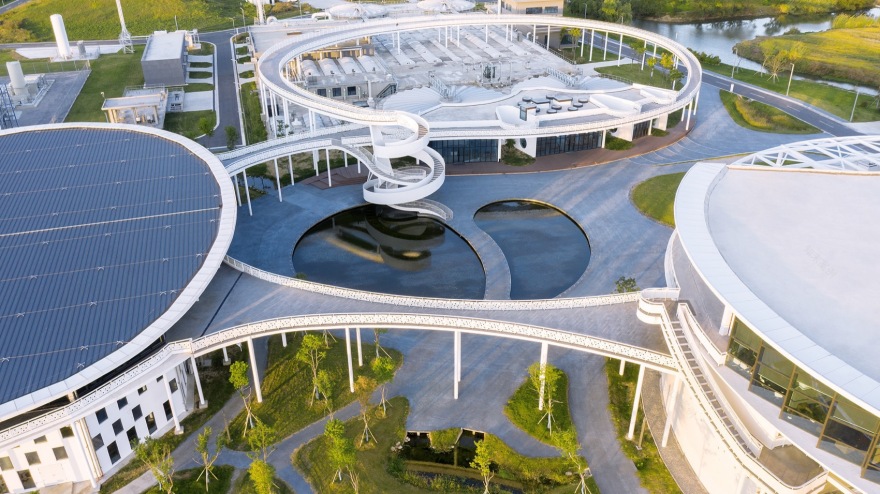
▼厂区东北侧鸟瞰,Aerial view of the northeast side of the project © 夏至
中国城市污水处理概念厂专家委员会,从2013年开始,几经酝酿,提出了“建设面向未来的中国城市污水处理概念厂”的构想,并明确了概念厂的四个追求“水质永续、能量自给、资源循环、环境友好”。
概念厂的整体建设包含污水处理(处理量20,000t/日)、污泥与有机质处理中心(处理量100t/日)、科学管理中心(5234m2)、实验线中试区等内容。整体建构筑面积约20,000m2,厂区的红线面积约8hm2。
The site of the project, surrounded by waters and farmlands, abounds in ecological resources. In the 8-hectare site for the plant, 20,000 square meters of structures have been built, including a sewage treatment plant with a capacity of 20,000 t/d, a sludge & OM treatment center with a capacity of 100 t/d, a science management center (5234 m2) and a pilot zone for experimental lines.
▼厂区整体及周边农田及水塘,
The whole plant and surrounding farmland and ponds
©夏至
厂区规划注重如下四点:高效布局集约用地;变传统治废为资源循环工厂;景观建筑一体化设计;“环境、社会,人文”全方位的可持续。
The overall planning of the plant is implemented in pursuit of an intensive layout, the efficient use of land, the integration of landscape & buildings, and the care for human.
▼ 厂区东侧鸟瞰,Aerial view of the east side of the project ©夏至
▼厂区整体及周边农田及水塘,
The whole plant and surrounding farmland and ponds
©夏至
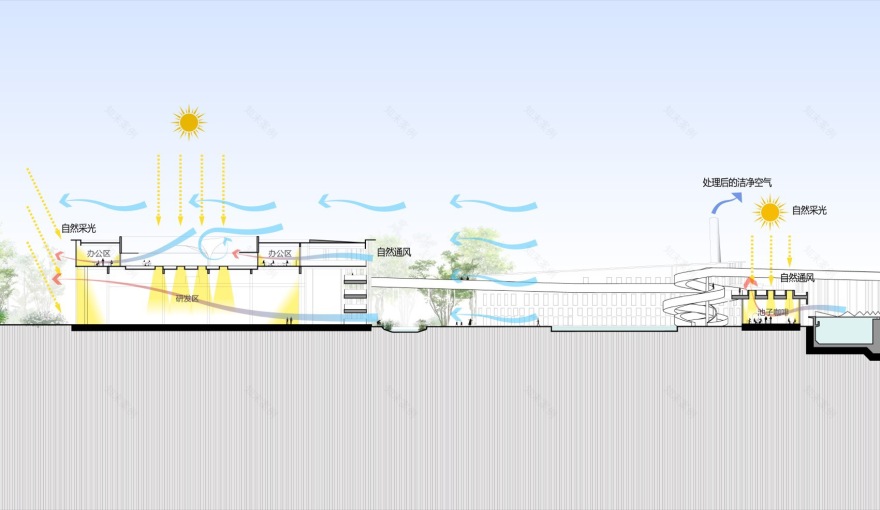
整体建筑分为三个组团:分别是北侧的水区(污水处理),西侧的泥区(污泥与有机质处理),东南侧的研发办公区。三个组团各自有独立的出入口及前场空间,并借助环绕中部共享的水务花园景观的参观连桥为纽带,将三个分散的单元串成整体。连桥的设置不仅能使人从更立体的角度了解污水资源工厂,同时将三个组团从空间上隔开,避免相互干扰,实现建筑景观一体化。
▼厂区整体集约布局优化,Optimization of the overall intensive layout of the plant ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
▼整体园区功能分区,Overall park functional zoning
©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
The waste water will be treated into clean water, fertilizers, and energies, such as biogas and thermal energy. The clean water will irrigate farmland and return to nature. The fertilizers and energies are sustainable products from waste resources.
▼ 概念厂与东侧鱼塘及垂钓者,Concept factory with east side fish pond and anglers ©夏至
▼ 厂区南侧农田与概念厂,Farmland on the south side of the concept factory ©夏至
▼入口区立体草坡景观与整体布局,Bird ‘s-eye view of the entrance to the factory © 夏至
▼ 厂区入口(看到研发办公楼与水区池子咖啡一角),Factory entrance (R & D office building and water area coffee corner) © 夏至
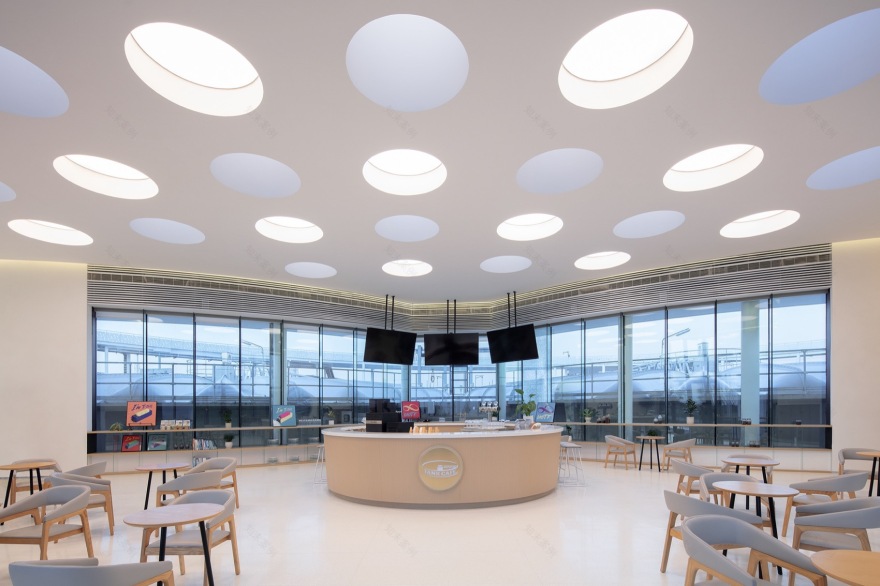
水区部分画龙点睛的处理是紧贴二沉池南侧的池子咖啡和中控展示厅这一线性序列空间。这部分不仅严丝合缝的与二沉池构筑物咬合,更是建筑,景观,室内,照明一体化的设计处理。咖啡区室内无柱的整体空间,配合不同时段的多功能布局,满足科普课堂,学术论坛,冷餐会等各种使用模式。
▼整体园区可持续设计策略,Overall sustainable design strategy ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
▼池子咖啡-天窗照明一体化设计详图,Coffee-skylight lighting integrated design detail drawing
©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
A special “Tank Cafe” clings to the southern wall of a secondary sedimentation tank. The specially designed space can also be transformed into a multi-functional conference hall or exhibition hall, serving for both professional and popular science activities.
Several small courtyards scattered in the coffee shop have optimized views and positions of openings while covering structural elements and separating different zones. Here, people can perceive, experience, or even play with its features, enjoying the changes of nature and the diversity of the ecological environment.
Through the project, the conservation of resources, the care for the environment, and the respect for humanity are spread to the public. The core value of the project lies in creating a conceptual plant that not only meets industrial demands but also serves as a public space that draws people close to it.
Here, people can perceive, experience, or even play with its features, enjoying the changes of nature, the diversity of the ecological environment, and the ever-changing patterns of light.
▼研发办公建筑南侧(底部研发中试区+顶部办公区),South side of R&D office building (bottom R&D pilot area + top office area) ©夏至
▼研发办公建筑东侧(底部研发中试区+顶部办公区),East side of R&D office building (bottom R&D pilot area + top office area) ©夏至
▼研发办公建筑去往泥区的架高廊桥,Elevated corridor bridge from the R&D office building to the mud area ©夏至
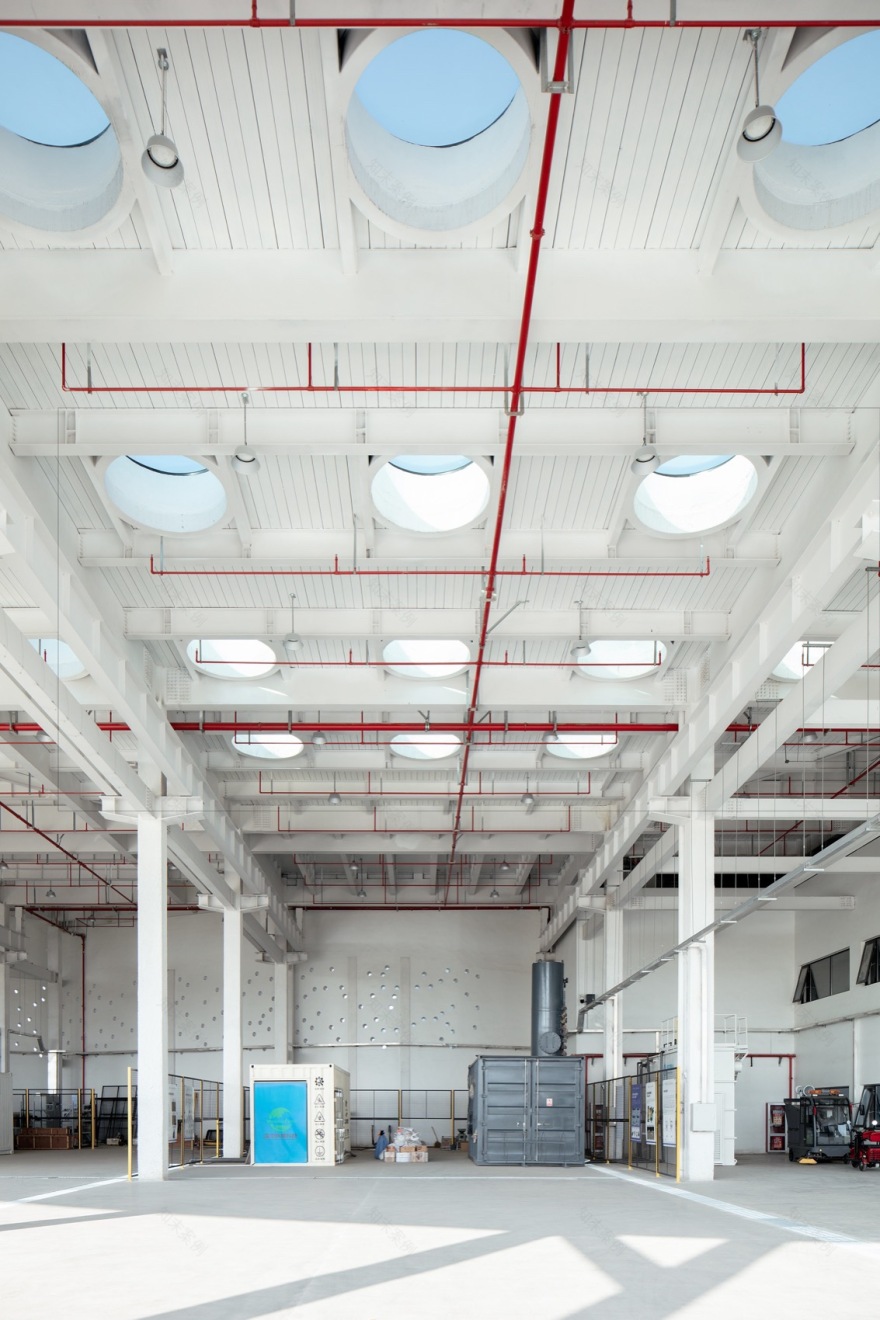
▼研发办公建筑底层中试区,Ground floor pilot area of the R&D building ©夏至
▼研发办公建筑底层半户外研发中试区,
Semi-outdoor pilot area on the ground floor of R&D office building ©夏至
▼ 池子咖啡天窗照明一体化设计,Pool coffee skylight lighting integrated design ©夏至
▼池子咖啡室内,Interior view of the coffee
©夏至
▼池子咖啡室内细部,Interior detailed view of the coffee
©夏至
▼池子咖啡侧墙圆窗,Side wall round window ©夏至
▼ 池子咖啡外侧梨形庭院,Pear-shaped courtyard outside the coffee ©夏至
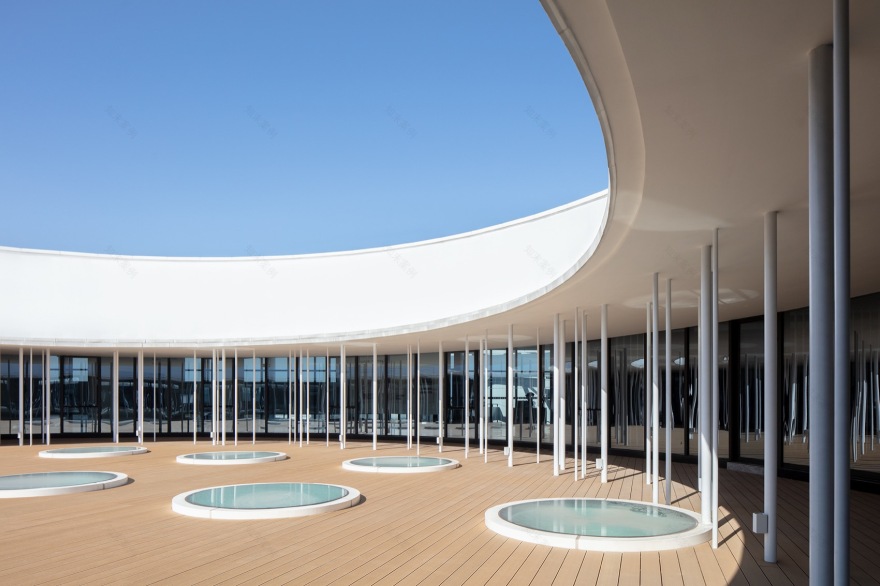
▼研发办公楼顶层圆形内院,
The circular inner courtyard on the top floor of the R&D office building ©夏至
立体的参观动线,自广场草坡而起,至广场水池双螺旋而终,将办公研发区,污水处理区,有机质处理区这三大功能板块环绕成一片抽象的“三叶草”。公众的参观与厂区的日常运行和维护界面立体分流,在保证公众可近距离观看各类处理工艺的前提下,不影响厂区内的安全生产与正常运营。
这一立体参观动线和公共广场的设立,加深了公众对概念厂的了解,增强了公众与工厂之间的互动:户外广场,草坡,景观水池可以办音乐节,文化周,户外婚礼,更多的参与开放的公众生活。
▼交通流线,Analysis diagram of circulation ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
Through the delicate spatial experience, concepts of the plant are conveyed to people, raising their awareness for the conservation of resources, the care for environment and the respect for humanity.
The overall planning and architectural design of the plant area respect and integrate the design of sewage and sludge treatment processes, and basically achieve the four goals of “water quality sustainability, resource recycling, energy self-sufficiency, and environmental friendliness”.
▼中心区从南向北鸟瞰,立体连廊串联三区,South to north bird’s eye view of the central area with three-dimensional corridor © 夏至
▼厂区整体及周边农田及水塘,Double helix and water area stereo corridor ©夏至
▼中央景观水池的双螺旋坡道,Double spiral ramp of central landscape pool © 夏至
▼双螺旋坡道上的参观团,Visiting group on the double spiral ramp ©夏至
▼双螺旋坡道从底部仰视,looks up toward the double spiral ramp © 夏至
▼双螺旋坡道底部空间,Bottom space of the double spiral ramp © 夏至
城市生活污水,经一系列水处理工艺净化后,达到卫生洁净标准的水,既可作为周边农田鱼塘的生态补给,实现生态环境中的水资源循环。同时净化过程中分离出的磷可以作为农业肥料的原材料,分离出的污泥与从城市里回收的餐厨垃圾和从周边农村回收的秸秆,禽畜粪便等有机废物混合后,通过特殊的处理工艺,产生沼气和有机物料。其中沼气可用于发电,用于厂区的能源供给,有机物料经处理后最终可成为营养土,有效实现城乡物资的良性循环。
▼资源回收循环,实现能源自给,Resource recycling cycle, energy self-sufficiency ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
▼厂区发电量及水区能耗自给率,Plant power generation and water area self-sufficiency rate of energy consumption ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
After a series of water treatment processes to purify urban domestic sewage with an average daily volume of 20000 tons, the water resources produced can be adapted to local conditions and maximally applied to urban and rural life production and ecological supply. The organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, and other nutrients produced can provide stable quality fertilizers for surrounding agriculture, planting, landscape, and other industries, drive their industrial upgrading towards green development, and effectively achieve a virtuous cycle of urban and rural materials.
Since the formal operation of the wastewater resource concept plant in October 2021, with the help of the comprehensive utilization model of "water fertilizer gas", and through continuous adjustment and optimization, the plant has achieved a self-sufficiency rate of 65% to 85% of the total energy in the plant area, and the water purification center has achieved 100% energy self-sufficiency.
▼研发办公建筑北侧入口广场区,R&D office building north entrance square area © 夏至
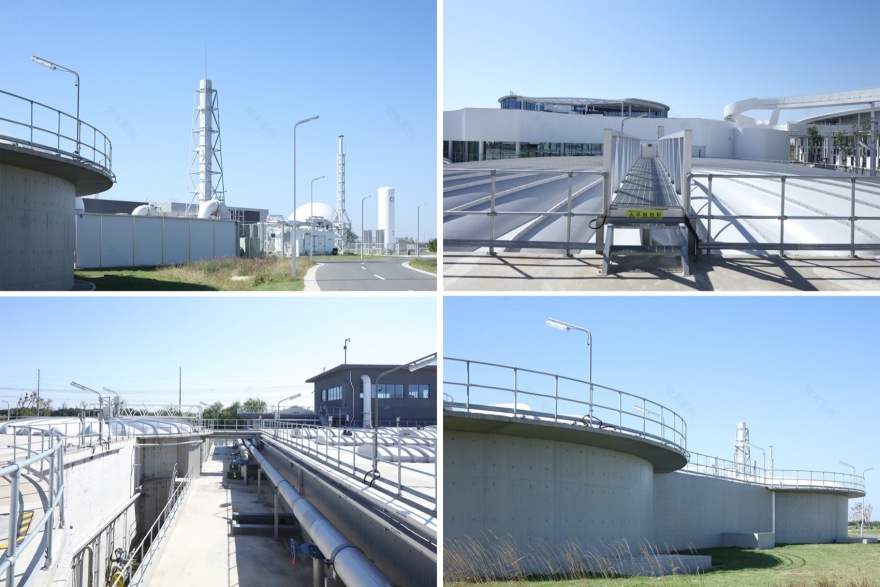
▼水区污水处理池顶看立体连廊,
Viewing the three-dimensional corridor from the water area sewage treatment tank
©夏至
▼研发办公建筑顶部空间,Top floor terrace of the R&D office building ©夏至
▼水区处理池的工业建造细节,Details of industrial construction of water treatment ponds ©夏至
▼泥区建筑与设备管线一体化设计,Integrated design of the mud area building and equipment pipeline
©夏至
项目建成后,也引发了国际不同专业背景专家们的关注和探讨:借助建筑和空间环境的整体设计,将一直隐藏的污水处理的资源价值,用直观的方式体现出来,让公众对环境基础设施建立新的认识,逐步接纳它们作为城乡资源循环和城市公共生活里重要而积极的一部分。
At the same time, it also marks another substantive achievement in the pursuit of “water quality sustainability, energy self-sufficiency, resource recycling, and environmental friendliness” by concept plants. And will set a far-reaching practical benchmark for relevant exploration in other regions of China.
▼厂区及周边农田及水塘,
The plant and surrounding farmland and ponds
©王志新
▼总平面图,Master plan ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
▼一层平面图,Ground floor plan ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
▼二层平面图,First floor plan ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
▼三层平面图,Second floor plan ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
▼剖面图,Section ©清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
项目名称:宜兴城市污水资源概念厂
项目地点:江苏省宜兴市
业主:中持新概念环境发展宜兴有限公司
设计单位:清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司素朴工作室
工程设计单位:民用建筑施工图设计: 清华同衡规划设计研究院有限公司
工业建筑施工图及工艺设计: 北京市市政工程设计研究总院有限公司
总建筑师:宋晔皓
主创建筑师:宋晔皓、孙菁芬
建筑设计团队:解丹(专业负责)石磊、陈晓娟、褚英男、吕蕙欣、 刘梦嘉(实习)、欧阳扬(实习)、 王希典(实习),林丹荔(实习),淮泽宇(实习)刘蕗(实习)
民用部分工程设计团队:温雅宸、舒涛、张彦红、张劲、张玥、郭毅、田英、尹大鹏、王鹏
建成状态:建成
设计时间(起迄年月):2018年8月~2020年6月
建设时间(起迄年月):2020年4月~ 2021年9月
用地面积(平方米):80302.5平方米
建筑面积(平方米):33484平方米
其他合作方:
景观双螺旋楼梯结构设计:和作结构建筑研究所 张准、张冲冲
照明设计:清华大学建筑设计研究院有限公司同原照明工作室
景观设计:北京雨人润科生态技术有限责任公司
施工单位:上海建溧建设集团有限公司
摄影师:夏至(主体照片), 王志新(使用及活动照片)
Project Name: Concept WRRF Yixing
Location: Yixing, Jiangsu Province, China
Client: CSD Water Service
Architect: SUP Atelier of THAD
Chief Architect: Song yehao, Sun jingfen
Design team: Xie dan, Shi lei, Chen xiaojuan, Chu yingnan, Loo huixin Liu Mengjia(Intern), Ouyang yang(Intern), Wang xidian(Intern), Lin danli(Intern), Huai zeyu(Intern), Liu lu (Intern)
Engineer Team: Wen Yachen, Shu tao, Zhang Yanhong, Zhang jin, Zhang yue, Guo Yi, Tian ying, Ying dapeng, Wang Peng
Under construction Design period: 2018.8-2020.6
Construction period: 2020.4-2021.09
Site area: 80302.5m2
Built area: 33484 m2
Engineer:
Civil building part: Tsinghua Tongheng Urban Planning & Design Institute
Industrial building part: Beijing General Municipal Engineering Design & Research Institute
Spiral landscape ramp Structure Desighn: AND Structure Office, Zhang zhun
Illumination design: ONE LIGHTING Studio of THAD
Landscape design: Beijing Yuren Raineco technology Co.,Ltd
Construction Contractor: Shanghai Jianli Group
Photograph: Xiazhi, Wang Zhixing( Photos in use)
客服
消息
收藏
下载
最近