查看完整案例

收藏
下载
Landscape Architecture for Sea Level Rise: Innovative Global Solutions|Texas A&M University
项目陈述
PROJECT STATEMENT
本书展示了应对洪水和海平面上升的创新措施,并提出了恰当的综合性多尺度防洪机制,以减少洪水影响。通过全球案例,本书展示并整理了实用且创新的结构型、非结构型以及混合型防洪机制。本书还提取并分析了替代性的洪水风险减缓机制,旨在制定增加洪水韧性的方法,而这些方法可以帮助新社区规划和现有社区保护。基于所呈现的信息,书中对工具、类型学和项目选项进行了分类和描述。本书还提出了一种新的设计理论——“城市危险区”。
This book showcases innovative measures for combating flooding and sea level rise. It identifies the appropriate mixture of integrated, multi-scalar flood protection mechanisms to reduce flood impacts. Illustrative, global cases identify and catalogue practical and innovative structural, non-structural, and hybrid mechanisms to combat flooding and sea level rise. Alternative flood risk reduction mechanisms are extracted and analyzed to develop approaches to increase flood resilience which can be applied to help proctor new and protect existing communities. As a result of the information presented, a set of tools, typologies, and program options are categorized and described. A new design theory, the urban periculum, is then presented.
▲本书封面,《应对海平面上升的景观:全球创新解决方案》Newman, G. & Qiao, X.主编 (2022年5月16日),伦敦Routledge出版社,Newman, G. & Qiao, X., eds. (May 16, 2022). Landscape Architecture for Sea Level Rise: Innovative Global Solutions. Routledge: London.Book Cover: Newman, G. & Qiao, X., eds. (May 16, 2022). Landscape Architecture for Sea Level Rise: Innovative Global Solutions. Routledge: London. © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
项目说明
PROJECT NARRATIVE
问题
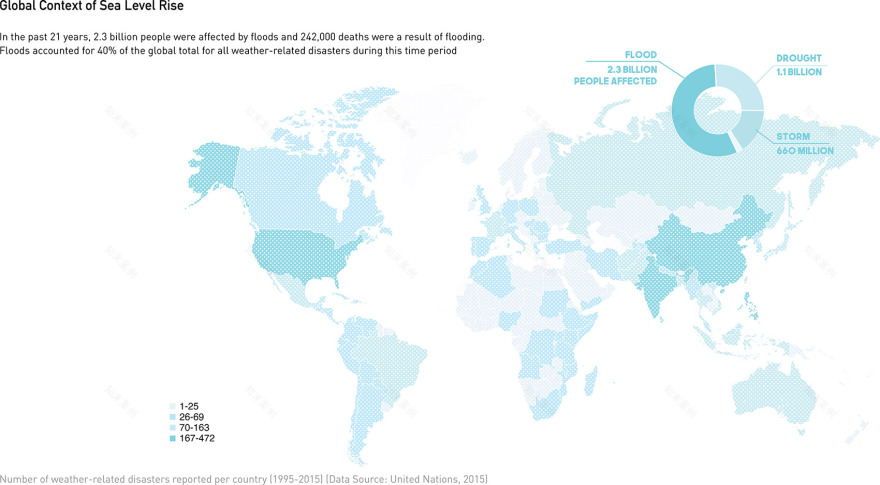
在过去21年中,洪水影响了23亿人,共造成24.2万人死亡。洪水已占据全球天气相关的自然灾害的40%。同时,由于海平面上升,洪水灾害的频率和强度也正在增加。预计到2100年,全球海平面将上升4至8英寸,沿海洪水灾害预计将增加一倍以上。
而沿海地区是美国人口密度最高的地区。美国20个最大城市中的14个、20个人口最密集的县中的19个都位于沿海地区。对于位于洪泛区或未来潜在洪泛区的人群,以及负责这些区域土地使用、开发和人口活动的利益相关方来说,为充分保护受威胁的区域,战略性地实施基于集成工程和绿色基础设施的防洪风险减缓机制就显得尤为重要。
方法/过程
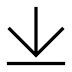
本书评估、展示并呈现了应对洪水和海平面上升的创新且实用的全球性措施。来自20所大学和8家景观建筑事务所的38位贡献者展示了一系列全球性典型项目,这些案例来自美国、韩国、澳大利亚、新西兰、泰国、日本、中国和荷兰。本书识别了应对海平面上升和洪水的创新性结构型(工程化)防洪机制、非结构型(基于自然)防洪机制和混合型防洪机制。本书从每一章中提取并分析了3大类、18个分类的共72个替代性洪水风险减缓机制的实例,以制定并阐明一套基于设计的类型学原理。
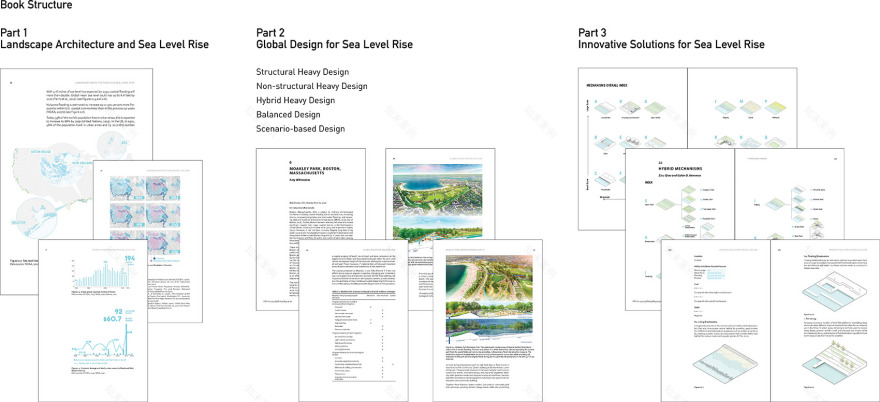
所有案例评估遵循相同的框架,以识别应对海平面上升的设计机制,并讨论以下内容:1) 地理区域内存在的问题;2) 海平面上升的预测;3) 设计方案的开发;4) 使用的防洪机制;5) 设计的影响/效果。全书分为三个部分。第一部分阐述了本书的立论依据和全球海平面上升的当前预测,同时讨论了解决这一问题的现有典型方法。第二部分呈现了全球性的深入案例研究。最后一部分提取、组织并分类了所呈现的机制,随后定义、可视化并描述了它们的主要特征和应用。最后,本书提出了一种新理论:城市危险区——指的是处于洪水风险和海平面上升威胁中的区域集合。
适用性与影响
本书描述了多种设计背景和适应策略,不仅拓宽了当局的选择,也超越了常规的做法(如垂直钢制挡水墙和堤坝)。本书旨在重新激发水本身的力量,超越工程化的成果,构思未来的景观,并打破“绿色与灰色”的对立,以进入设计与赋权的新领域。书中为景观建筑师提供了一个比较性背景,供其参考并拓展解决问题的思路。本书迅速成为设计师群体中影响力巨大的资源,也成为制定洪水风险减缓计划的宝贵要素集合,也成为学生、教师和专业人士的必备读物。美国景观建筑师协会(ASLA)将其评选为2022年度最佳图书,称其创造了一个有价值的工具包,能够帮助设计师应对未来的气候变化。因此,本书对学术界和涉及多个设计专业的从业者都有重要的帮助。
▲书籍摘录:混合机制分类方案,Classification Scheme for Hybrid Mechanisms:Book Excerpt: Classification Scheme for Hybrid Mechanisms © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
© Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:书籍的三大主要部分,Three Primary Sections of the Book:Book Excerpt: Three Primary Sections of the Book © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:全球海平面上升背景-天气相关灾难,Global Context of Sea Level Rise – Weather Related Disasters,Book Excerpt: Global Context of Sea Level Rise – Weather Related Disasters © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:全球海平面上升背景-预计海平面上升,Global Context of Sea Level Rise – Projected Sea Level Rise,Book Excerpt: Global Context of Sea Level Rise – Projected Sea Level Rise © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:全球海平面上升背景-案例位置,Global Context of Sea Level Rise – Case Locations,Book Excerpt: Global Context of Sea Level Rise – Case Locations © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:海平面上升设计机制总体索引,Overall Index for Design Mechanisms for Sea Level Rise:Book Excerpt: Overall Index for Design Mechanisms for Sea Level Rise © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:坦帕(佛罗里达州)的机制与方案分解-结构型设计,A Breakdown of Mechanisms and Program for Plan in Tampa Florida – Structural Heavy Design:Book Excerpt: A Breakdown of Mechanisms and Program for Plan in Tampa Florida – Structural Heavy Design © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:波士顿(麻萨诸塞州)机制与方案分解-非结构型设计,A Breakdown of Mechanisms and Program for Plan in Boston, MA – Non-structural Heavy Design:Book Excerpt: A Breakdown of Mechanisms and Program for Plan in Boston, MA – Non-structural Heavy Design © Amy Whitesides
▲书籍摘录:曼谷(泰国)机制与方案分解-混合型设计,A Breakdown of Mechanisms and Program for Plan in Bangkok, Thailand – Hybrid Heavy Design:Book Excerpt: A Breakdown of Mechanisms and Program for Plan in Bangkok, Thailand – Hybrid Heavy Design © Sani Limthongsakul, Pudtan Chantarangkul, and Supreeya Wungpatcharapon
▲书籍摘录:休斯顿(佛罗里达州)机制与方案分解-平衡型设计,A Breakdown of Mechanisms and Program for Plan in Houston, FL – Balanced Heavy Design:Book Excerpt: A Breakdown of Mechanisms and Program for Plan in Houston, FL – Balanced Heavy Design © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:海平面上升应对机制的分类示例-结构机制,An Example of the Cataloging of Mechanisms Covered for Combating Sea Level Rise – Structural Mechanisms:Book Excerpt: An Example of the Cataloging of Mechanisms Covered for Combating Sea Level Rise – Structural Mechanisms © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:海平面上升应对机制的分类示例-混合机制,An Example of the Cataloging of Mechanisms Covered for Combating Sea Level Rise – Hybrid Mechanisms:Book Excerpt: An Example of the Cataloging of Mechanisms Covered for Combating Sea Level Rise – Hybrid Mechanisms © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:海平面上升应对机制的分类示例-非结构机制,An Example of the Cataloging of Mechanisms Covered for Combating Sea Level Rise – Non-structural Mechanisms:Book Excerpt: An Example of the Cataloging of Mechanisms Covered for Combating Sea Level Rise – Non-structural Mechanisms © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
▲书籍摘录:城市危机——应对海平面上升风险的新理论,The Urban Periculum – A New Theory for Combating Landscapes at Risk from Sea Level Rise:Book Excerpt: The Urban Periculum – A New Theory for Combating Landscapes at Risk from Sea Level Rise © Galen Newman and Zixu Qiao
Project Narrative
Problem
In the past 21 years, 2.3 billion people were affected by floods, 242,000 deaths resulted from flooding, and floods accounted for 40% of the global total for weather-related disasters. The frequency and magnitude of flood events is increasing due to rising sea levels. Up to 4–8 inches of global sea level rise is projected by 2100, with coastal flooding also projected to more than double. Further, coastal areas have the highest population density in the US, with 14 of the nation’s 20 largest cities and 19 of the 20 most densely populated counties occupying the coast. It is important for those located in the floodplain or future floodplain and those responsible for land use, developmental, and population-related activities within these areas to strategically implement integrated constructed and green infrastructure-based flood risk reduction mechanisms to adequately protect threatened areas.
Methods/Process
This book assesses, illustrates, and presents innovative and practical worldwide measures for combating flooding and sea level rise. Thirty-eight contributors from 20 Universities and 8 landscape architecture offices present a series of illustrative global projects from the United States, Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Japan, China, and the Netherlands and identify novel structural (engineered), non-structural (nature-based), and hybrid mechanisms (mixed) to combat sea level rise and flooding. Three categories, 18 classifications, and 72 examples of alternative flood risk reduction mechanisms are extracted and analyzed from each chapter to develop and explain a set of design-based typologies.
All case evaluations follow an identical framework to identify the design mechanisms to combat sea level rise and discuss 1) the problems within the geographic region, 2) sea level rise projections, 3) the design developed, 4) the flood mechanisms utilized, and 5) the impact/performance of the plan. The book is arranged into three parts. The first section provides the rationale for the book and current sea level rise projections globally, while discussing existing typical approaches to solving the issue. Section 2 presents the in-depth, global case studies. The final section extracts, organizes, and classifies the presented mechanisms, then defines, visualizes, and describes their primary characteristics and uses. Finally, the book presents a new theory: the urban periculum – a collection of areas that are at risk of flood hazards and sea level rise.
Applicability and Impact
The book describes a range of contexts and adaptation strategies that expand options for authorities beyond business-as-usual approaches such as vertical steel bulkhead walls and levees. It seeks to reclaim the power of water itself and look beyond engineered outcomes to conceive future landscapes that move beyond green vs gray and into new imaginative territories of design and empowerment. The book provides a comparative context for landscape architects to draw from to expand the problem-solving mix. It has rapidly become a highly influential resource for designers, a valuable collection of programmatic elements for developing mitigation plans, and a must-have for students, instructors, and professionals. ASLA designated it as a Top Book of 2022, stating that it creates a valuable toolkit that can help designers combat future climate change. As a result, the book is beneficial to both academics and practitioners related to multiple design professions.
Project Credits
Zixu Qiao, Co-editor of Book
More:ASLA ;德克萨斯农工大学 Texas A&M University
客服
消息
收藏
下载
最近