查看完整案例

收藏
下载
项目名称:UNIT.City工业区转型
位置:乌克兰
设计单位:KOTSIUBA
图片数量:17张
项目陈述Project Statement
UNIT.City将一处后工业场地转型为创新城区,使教育、工作与公共生活在此无缝交汇。项目重新激活了一片曾经封闭受限的区域,打造出一个以步行为导向、适应气候变化的城市环境,并显著增强了与城市整体的连接性。
以景观为先导的设计策略塑造了核心公共空间体系——包括活动广场、步行街道、教育中心与雨水花园——促进了社会交往、生物多样性与城市韧性。通过强调友好步行尺度与绿色基础设施,UNIT.City为具备适应性和可持续性的城市更新树立了标杆,重新定义了城市如何将工业遗产转化为面向未来的活力城区。
UNIT.City transforms a post-industrial site into an innovation district where education, work, and public life seamlessly intersect. The redevelopment reclaims a once-restricted area, establishing a walkable, climate-responsive urban environment that enhances connectivity with the city.
A landscape-first approach defines key public spaces — including Event Plaza, pedestrian streets, an education hub, and rain gardens — that foster social interaction, biodiversity, and urban resilience. By prioritizing pedestrian-friendly design and green infrastructure, UNIT.City sets a precedent for adaptive, sustainable urban transformation, redefining how cities repurpose industrial heritage into thriving, future-ready districts.
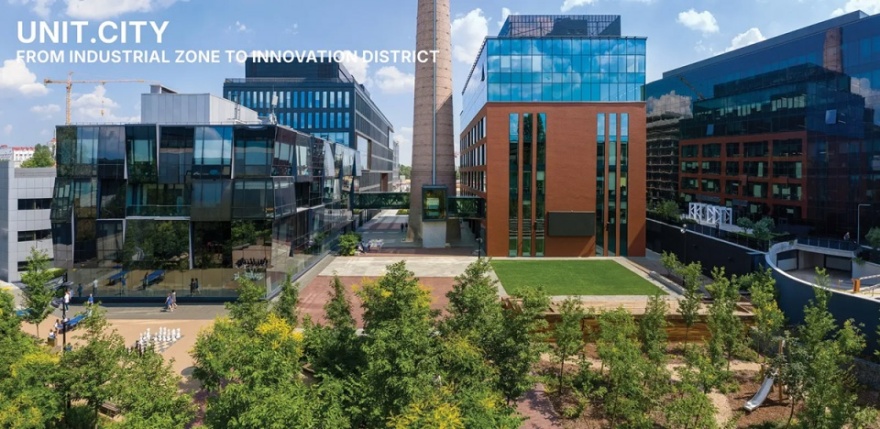
▲一处工业用地被转变为开放式城市校园,使教育、工作与公共生活在此融合共生。The transformation of an industrial area into an open urban campus integrating education, work, and public life.© Ivan Avdeenko
项目说明PROJECT NARRATIVE
UNIT.City:从工业用地到创新城区的转型
引言:工业遗址上的新城市空间
UNIT.City为一处旧工业用地重新注入活力,使其转型为乌克兰的首个创新城区,在这里,教育、工作与公共生活相互交织。项目通过重新向公众开放曾经受限的场地,为适应性城市发展与可持续城市营造提供了示范。景观设计作为转型的核心驱动力,提升了步行连通性、城市韧性与整体空间体验,塑造出一个可应对气候变化的公共环境。
背景与城市挑战
对60英亩原工业制造基地的更新,回应了三项核心城市议题:场地再融入:将曾经孤立的工业区重新连接至基辅不断演变的城市肌理;工业遗产的延续:在尊重历史脉络的基础上,转化其价值,构建面向未来的创新生态系统;塑造具备气候韧性的公共领域:打造行人优先、包容开放的空间,促进社会、教育与经济活动的发生。
这种工业遗产与创新精神之间的平衡,共同定义了该片区独特的城市身份。
城市框架:核心公共空间体系
一套连续的公共空间网络确保了城市整合与步行连通性:活动广场:可灵活使用的市民空间,满足日常活动与大型公共事件;步行街道:连接居住、商业与教育功能的慢行网络;教育中心:面向学习、协作与研究的开放式校园空间;校园与雨水花园:将生态教育与可持续雨洪管理融入日常环境。
这些空间不仅承担着功能角色,还能够激活社区生活、强化生态网络,构建富有韧性的城市结构。
设计原则与整合策略
UNIT.City的设计遵循三项核心城市策略:以行人为先的空间组织:共享空间优先服务人,而非车辆;灵活的景观系统:多功能空间支持工作、休闲与社交活动;材料语言的表达:耐候钢、混凝土与木材回应工业历史,同时塑造当代城市形象。
在UNIT.City中,景观并非附属元素,而是塑造城市空间的关键力量。
生态韧性:适应气候的景观体系
该项目通过基于自然的解决方案提升了环境功效:缓冲型景观带:缓解热压力、降低噪声并改善微气候;雨水花园:在管理雨洪的同时提升生物多样性;多样化植物配置:降低维护成本并改善空气质量。
这些策略共同提升了城市的生态韧性与宜居性。
社会激活与公共生活
UNIT.City构建了充满活力的公共领域,营造引人参与的城市体验:文化活动策划:节庆、音乐会与公共表演;户外与学习空间:在灵活环境中促进交流与合作;无障碍设计:包容性的空间体系,欢迎所有使用者。
通过以人为本的设计理念,项目确保了公共空间的持续活力与高度连通性。
结语:创新与城市转型的示范
UNIT.City为后工业用地的再开发树立了新标杆,它展现了城市更新如何驱动创新与经济增长、高质量公共空间如何增强城市连接性与社会参与,以及可持续景观如何提升气候韧性与城市宜居性。
UNIT.City证明了以景观引导的城市主义能够将后工业地区转化为充满活力、具备韧性、面向未来的城市片区。
▲借助公共空间体系与以步行为导向的基础设施,曾经的制造业片区逐步重新融入了城市肌理。A former manufacturing zone is gradually reintegrated into the urban fabric through public spaces and pedestrian-friendly infrastructure.© APA Wojciechowski Architekci, KOTSIUBA
▲由活动广场、步行街道与教育中心等主要空间构成的网络,为学习、工作与社会交往营造出充满活力的场所。A network of key spaces—including the Event Plaza, pedestrian streets, and Education Hub—creates a dynamic space for learning, work, and social life.© APA Wojciechowski Architekci, KOTSIUBA
▲灵活可变的广场将人们聚集在一起,承载日常活动、社交互动与文化事件,塑造生机勃勃的城市空间。A flexible plaza that brings people together for daily activities, social gatherings, and cultural events, creating a vibrant and dynamic urban space.© UNIT.City, Maria Savoskula, KOTSIUBA
▲多层次座椅、绿植与开放式聚集空间,共同营造出适宜休憩、活动与交流的友好场所。Multi-level seating, greenery, and open-air gathering spaces create a welcoming setting for leisure, events, and social engagement.© Maria Savoskula, Ivan Avdeenko
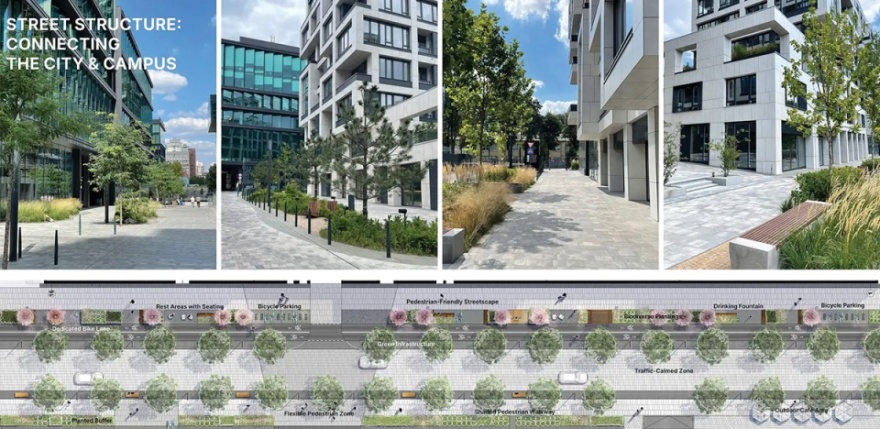
▲UNIT.City的街道体系通过共享空间理念与主动式绿色基础设施,打造适合步行与骑行的城市环境。UNIT.City’s street network promotes a walkable and cyclist-friendly environment through shared space principles and active green infrastructure.© KOTSIUBA, Maria Savoskula
▲宽敞的人行道、绿色缓冲带与直观清晰的路径组织,实现创新城区与城市之间的无缝衔接。Wide sidewalks, green buffers, and intuitive pathways create seamless transitions between the innovation district and the city.© KOTSIUBA
▲通过整合高校、研究机构与灵活的学习空间,校园环境促进科技发展与跨界协作。Integrating academic institutions, research centers, and flexible learning spaces, the campus fosters technology development and collaboration.© Ivan Avdeenko, Maria Savoskula, KOTSIUBA
▲空间既满足结构化教学需求,也支持非正式交流,激发创造力并鼓励户外活动。Designed to accommodate both structured education and informal collaboration, fostering creativity and outdoor engagement.© Maria Savoskula, Ivan Avdeenko
▲绿色空间与建筑环境交织,提供遮荫、缓冲与自然休憩场所。Green spaces are woven into the built environment, providing shaded areas, buffer zones, and natural retreats for relaxation.©Maria Savoskula
▲高密度的城市森林可提升生物多样性、调节微气候,并在城市中构建可持续运作的自然生态系统。A dense urban forest that enhances biodiversity, regulates the microclimate, and creates a self-sustaining natural ecosystem within the city.©Maria Savoskula, KOTSIUBA
▲植被能够有效降低噪声、缓解热量积聚并改善空气质量,营造更健康、舒适的城市环境。Vegetation mitigates noise, reduces heat accumulation, and improves air quality, fostering a healthier and more comfortable urban environment.© Maria Savoskula
▲场地为游乐、运动与互动而设计,从户外棋类、乒乓球到健身区与儿童游乐场,满足多样使用需求。Designed for play, movement, and interaction — from outdoor chess and table tennis to workout zones and playgrounds.© Maria Savoskula, Ivan Avdeenko
▲节庆、音乐会与社区活动持续为UNIT.City注入活力,营造全年开放的生动城市氛围。Festivals, concerts, and community events bring UNIT.City to life, creating an active and engaging urban atmosphere year-round.© UNIT.City
▲耐候钢、混凝土与木材延续了场地的工业记忆,同时塑造出现代而鲜明的城市形象。Corten steel, concrete, and wood honor the site’s industrial past while shaping a modern and distinctive urban character.© Maria Savoskula, Ivan Avdeenko, KOTSIUBA
▲校园将雨水花园与绿色空间融入教学环境,有助于促进生态意识培养与实践式学习体验。The school integrates rain gardens and green spaces, promoting ecological awareness and hands-on learning experiences.© KOTSIUBA
客服
消息
收藏
下载
最近




















