查看完整案例


收藏
下载
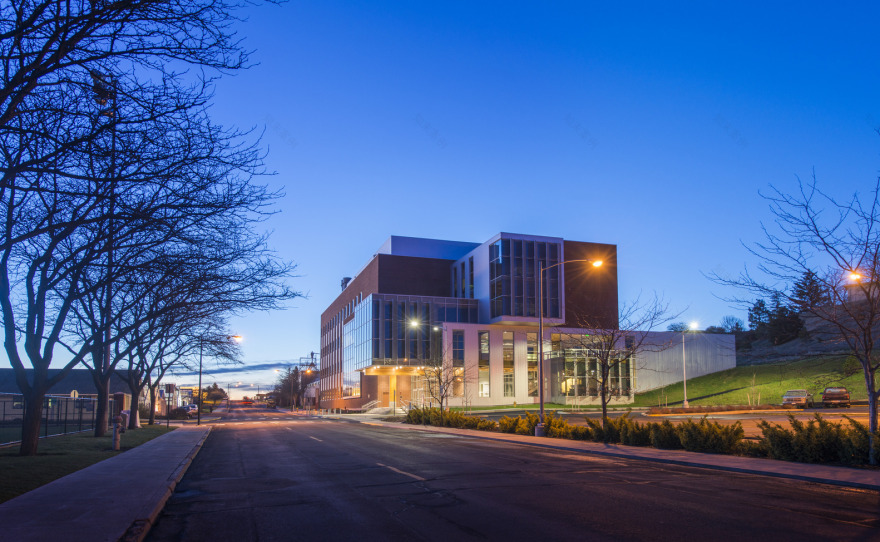
架构师提供的文本描述。位于华盛顿州普尔曼的华盛顿州立大学的环境技术大楼耗资5 280万美元,使世界首脑会议的“沃兰工程和建筑学院”的愿景得以实现,并开展了与可持续性问题有关的跨学科研究。这个96,000平方英尺的项目是设计师、LMN建筑师和总承包商Skanska之间的合作项目.这座四层楼的建筑服务于WSU的五个长期研究和开发中心,所有这些中心都致力于通过跨学科合作来解决多方面的环境问题。“这个项目令人兴奋的地方在于它如何总结了当代教育的许多内容-合作,探索…一个真正的跨学科方法-整个项目本质上是一个巨大的实验室,“LMN合伙人马克·雷丁顿(MarkReddington)指出。
Text description provided by the architects. The $52.8 million PACCAR Environmental Technology Building at Washington State University in Pullman, Washington brings to life the vision of WSU’s Voiland College of Engineering and Architecture and the pursuit of interdisciplinary research related to sustainability concerns. The 96,000-square-foot project is a collaboration between designers LMN Architects and general contractor Skanska. The four-story building serves five of WSU’s long-standing research and development centers, all dedicated to tackling multi-faceted environmental issues through interdisciplinary collaboration. “What’s exciting about this project is how it sums up so much of what contemporary education is about—collaboration, exploration…a true interdisciplinary approach—the whole project is essentially one giant laboratory,” notes Mark Reddington, FAIA, Partner at LMN.
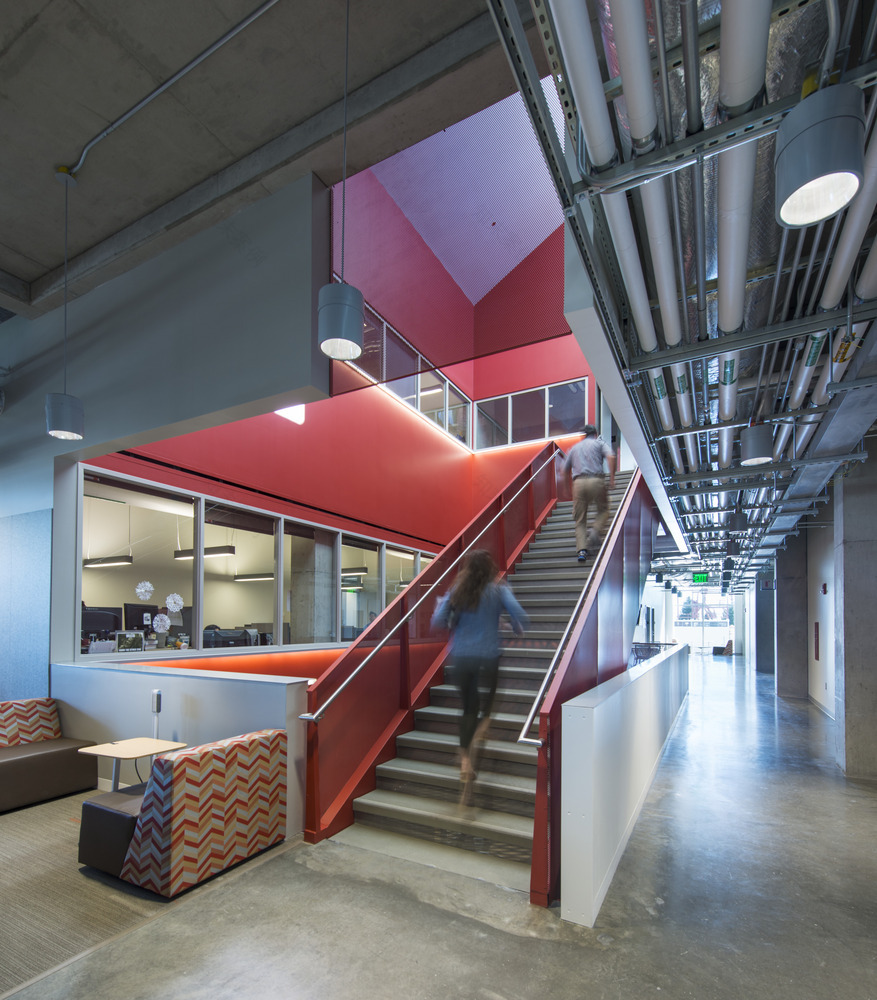
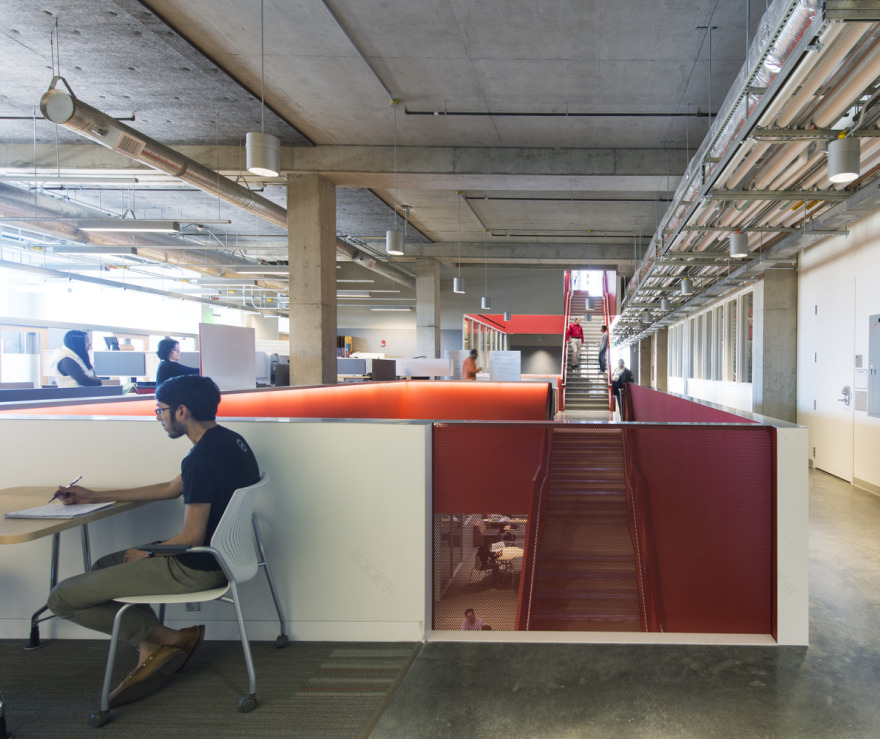
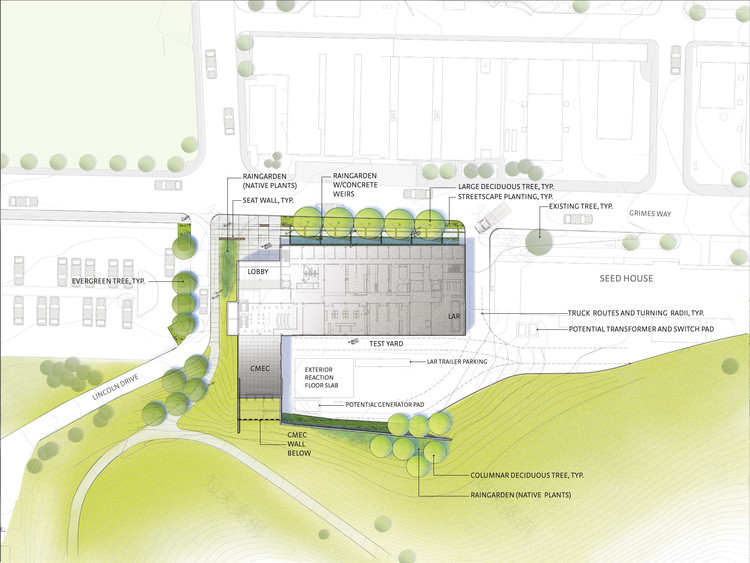
从概念上讲,建筑将合作精神与物质性探索融为一体。在功能上,这座建筑由两个不同的元素组成:一个“工作吧”,内有安全的实验室、办公室和学生工作站;另一个“展示栏”,以透明的程序空间向校园社区展示该项目的工作,包括一个重型材料实验室、一个双高研究室和一个灵活的设计工作室。两个酒吧的交汇处创建了一个“城市广场”,一个休息室和咖啡厅,作为该项目的社会中心,一般公众和研究人员可以在那里混合和欣赏校园、Palouse和活动空间的景观。
Conceptually, the building merges the spirit of collaboration with the exploration of materiality. Functionally, the building is formed by two distinct elements: a “workhorse bar” housing secure laboratories, offices, and student workstations; and a “showcase bar” that presents the program’s work to the campus community with transparent program spaces, including a heavy materials lab, a double-height seminar room, and a flexible design studio. The intersection of the two bars creates a “Town Square,” a lounge and cafe that serve as the social hub of the program and where the general public and researchers can intermingle and enjoy views of the campus, the Palouse, and the active spaces.
© Ed LaCasse
C.Ed LaCasse
© Ed LaCasse
C.Ed LaCasse
建筑物的西部部分,包括辛普森强领带研究和测试实验室,是由工程木制品构成的,包括交叉层压木材(Clt),以及胶合木和层合单板木材。这些工程木制品的历史与WSU有着千丝万缕的联系。其中一个研究中心,复合材料和工程中心(CMEC),是木材材料和工程实验室的现代接班人,该实验室于1949年在WSU成立,在发展价值10亿美元的木材工业中发挥了重要作用。“参与一个项目是令人兴奋的,从本质上讲,它是为了拓展建筑材料未来的界限。”雷丁顿说。
The western portion of the building, including the Simpson Strong-Tie® Research and Testing Laboratory, is framed in engineered wood products including cross-laminated timber (CLT), as well as glue-laminated timber and laminated-veneer lumber. The history of these engineered wood products is intricately tied to WSU. One of the research centers, the Composite Materials and Engineering Center (CMEC), is the modern successor to the Wood Materials and Engineering Laboratory, which was founded at WSU in 1949 and was instrumental in the development of the billion-dollar industry of up-cycling wood waste from the timber industry. “It is exciting to be involved in a project that, at its essence, is about pushing the boundaries of what the future holds for building materials.” says Reddington.
© Ed LaCasse
C.Ed LaCasse
© Ed LaCasse
C.Ed LaCasse
捕捉到的雨水满足了85%的非饮用水需求,日光通过数字化模型的太阳镜校准,使无眩光全景景观成为可能。这座建筑占据了未来WSU学术核心发展的关键位置,为校园这一部分的校园建设环境的特色树立了先例。该设计强调社区的感觉,促进步行能力,街道层面的接触,并连接到自然景观。该项目是LEED黄金认证。
Captured rainwater satisfies 85 percent of the non-potable water demand, and daylight is calibrated through digitally-modeled sunshades making glare-free, panoramic views possible. Occupying a key site in the future growth of WSU’s academic core, the building sets a precedent for the character of the university’s built environment destined for this part of campus. The design emphasizes a neighborhood feel that promotes walkability, street-level encounters, and connections to the natural landscape. The project is LEED Gold Certified.
© Ed LaCasse
C.Ed LaCasse
Architects LMN Architects
Location Pullman, WA 99163, United States
Category Industrial Architecture
Area 96000.0 ft2
Project Year 2017
Photographs Ed LaCasse
Manufacturers Loading...
客服
消息
收藏
下载
最近