查看完整案例


收藏
下载
Courtesy of MIT Mass Timber Design
麻省理工学院大众木材设计
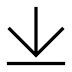
长屋-顾名思义-是一座狭长的建筑,通常包含一个单独的公共空间,用于公民活动或团体活动。建筑方面的挑战是跨越这么大的距离,空间内很少或没有中断,因此房间保持尽可能的灵活性和适应性。该团队的设计使用了一系列木材叠合单板木材(LVL)拱门跨越建筑的短段,与拱门的薄壁三角形轮廓提供了最佳的刚性结构。数控加工的预制模块化系统被用于其剩余的大部分元件,这使得一个整体高效的装配,大大减少了在现场所花费的时间。所创造的广阔空间将被用于多种不同的方式,包括合作,锻炼课程,社交混合器,展览,晚餐聚会和讲座。
Longhouses - by their very definition - are long, narrow building, usually containing a single communal space used for civic or group activities. The challenge in construction is spanning such a large distance with little or no disruption within the space so that the room remains as flexible and adaptable as possible. The team’s design uses a series of timber laminated veneer lumber (LVL) arches across the short section of the building to achieve this, with the arch’s thin-walled triangular profile providing optimum rigidity for the structure. A CNC manufactured prefabricated modular system is employed for the majority of its remaining elements, which makes for an overall efficient assembly, greatly reducing the time spent on-site. The expansive space created will be used in multiple different ways, including co-working, exercise classes, social mixers, exhibitions, dinner gatherings, and lectures.
Courtesy of MIT Mass Timber Design
麻省理工学院大众木材设计
Courtesy of MIT Mass Timber Design
麻省理工学院大众木材设计
Courtesy of MIT Mass Timber Design
麻省理工学院大众木材设计
在建筑环境面临巨大变化的时刻,对能源智能建筑原型的需求比以往任何时候都更加重要。
At [a] moment when the built environment is faced with dramatic shifts, the need for energy-intelligent building prototypes is more significant than ever.
大量木材最近流行程度的增长很大程度上可以归因于它对环境的巨大好处。长屋的设计建立在这些品质的基础上,不仅设计了一个可持续的项目,而且还设计了一个产生能量的项目。“锯齿屋顶”的角度和定位的方式,以最大限度地增加太阳能和日光需求,而一个低的窗墙比保持一个有效的,绝缘的热包膜。麻省理工学院大众木材设计团队致力于此类项目的进一步开发和研究,继续探索“建筑与技术交叉处可持续建筑的未来”。
Mass timber’s recent growth in popularity can be largely attributed to its significant environmental benefits. The Longhouse design builds upon these qualities, designing not only a sustainable project but one that produces energy. The “sawtooth roof” is angled and orientated in such a way to maximize solar gains and daylight needs, while a low window-to-wall ratio maintains an efficient, insulated thermal envelope. The MIT Mass Timber Design team are committed to the further development and research of projects like this, continuing to explore “the future of sustainable buildings at the intersection of architecture and technology.”
Courtesy of MIT Mass Timber Design
麻省理工学院大众木材设计
Courtesy of MIT Mass Timber Design
麻省理工学院大众木材设计
建筑师麻省理工学院(MIT)大众木材设计研究科学家JohnKlein设计-工程团队JohnFechtel、PaulShort、Demang、AndrewBrose、HyerinLee、AlexandreBeaudouin-MackayEngineeringBurohapold工程合作者NovaConcepts大学MIT的建筑领域的DepartmentofArchitectureArea680.0M2项目年2018年
Architects MIT Mass Timber Design Research Scientist John Klein Design-Engineering Team John Fechtel, Paul Short, Demi Fang, Andrew Brose, Hyerin Lee, Alexandre Beaudouin-Mackay Engineering BuroHappold Engineering Collaborator Nova Concepts University MIT’s Department of Architecture Area 680.0 m2 Project Year 2018
新闻来源:麻省理工学院。
News via: Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
客服
消息
收藏
下载
最近